Group Managed Service Accounts in Windows Server 2012
The technology of Managed Service Accounts (MSA) was firstly introduced in Windows Server 2008 R2 to automatically manage (change) passwords of service accounts. Using Managed Service Accounts, you can considerably reduce the risk of system accounts running system services being compromised. (It’s no secret that there are a lot of utilities that allow to extract locally passwords of users from LSASS).
For MSA accounts, a password containing 240 characters is generated, half of which are English letters and another half is special characters. The password for this type of account is changed automatically (by default, every 30 days) and is not stored on the local system.
One of the main MSA drawbacks is the opportunity to use such service account only on one computer. It means that MSA service accounts cannot work with cluster or NLB services (web farms) which operate simultaneously on multiple servers and use the same account and password
To eliminate this drawback, Microsoft added the feature of Group Managed Service Accounts (gMSA) to Windows Server 2012. These accounts can be used simultaneously on several servers, so that all service instances used the same account, like in Load Balancer (NLB), cluster services, etc.
gMSA Requirements:
To use gMSA features, the infrastructure has to meet the following requirements:
- The level of AD schema has to be Windows Server 2012
- Windows Server 2012 (or later) domain controller with Microsoft Key Distribution Service — this service is responsible for password generation
- PowerShell module to manage Active Directory
- Windows Server 2012/2012 R2 and Windows 8/8.1 can be used as clients
- The service using gMSA has to be compatible with this type of the accounts. (It has to be specified in the documentation.) Today gMSA is supported by SQL Server 2008 R2 SP1, 2012;IIS; AD LDS; Exchange 2010/2013
How to Create a KDS Key
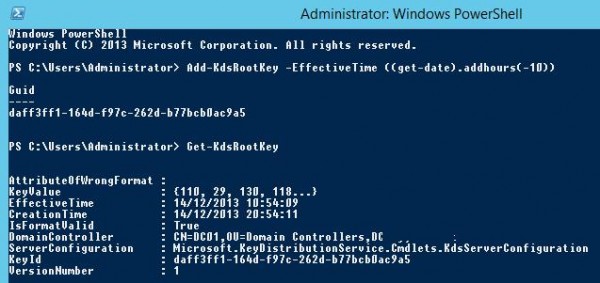
Before you start creating an account gMSA, you must to perform a one-time operation and create a KDS root key. To do it, run the following command with administrator privileges on the domain controller (Microsoft Key Distribution Services has to be installed and running):
In this case the key is created and becomes available in 10 hours after the replication is over.
Add-KdsRootKey –EffectiveImmediatelyIn this case the key is created and becomes available in 10 hours after the replication is over.
Tip. To use the key immediately in the test environment, you can run this command:
Add-KdsRootKey –EffectiveTime ((get-date).addhours(-10))How to Create a gMSA Account
Create a new gMSA account with the following command:
Where gmsa1 is the name of the gMSA account to be created
New-ADServiceAccount -name gmsa1 -DNSHostName dc1.woshub.com -PrincipalsAllowedToRetrieveManagedPassword "gmsa1Group"Where gmsa1 is the name of the gMSA account to be created
dc1.woshub.com is the DNS server name
gmsa1Group is an Active Directory group that includes all systems which are going to use this group account. (The group has to be created in advance.)
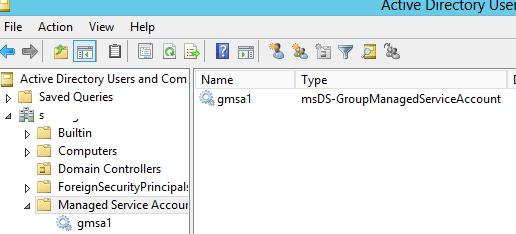
After the command has been executed, open the ADUC (Active Directory Users and Computers) console and make sure that the corresponding account has appeared in Managed Service Accounts container (OU). (By default, this container is hidden. To see it, enable Advanced Features in the View menu of the snap-in.)
How to Install gMSA on a Server
Enable Powershell module to support Active Directory environment:
Then you have to install the managed account on the servers, on which it will be used. (With this account, a service is going to be run.) First of all, make sure that this server is allowed to get a gMSA account password from Active Directory. To do it, its account has to be a member of the domain group specified when creating the account (in our case it is gmsa1Group). Install gmsa1 account on this server:
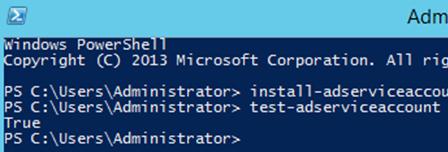
You can make sure if the group service account is installed correctly using this command (for Windows PowerShell 4.0):
If the command returns True, it is configured correctly.
Add-WindowsFeature RSAT-AD-PowerShellThen you have to install the managed account on the servers, on which it will be used. (With this account, a service is going to be run.) First of all, make sure that this server is allowed to get a gMSA account password from Active Directory. To do it, its account has to be a member of the domain group specified when creating the account (in our case it is gmsa1Group). Install gmsa1 account on this server:
Install-ADServiceAccount -Identity gmsa1You can make sure if the group service account is installed correctly using this command (for Windows PowerShell 4.0):
Test-ADServiceAccount gmsa1If the command returns True, it is configured correctly.
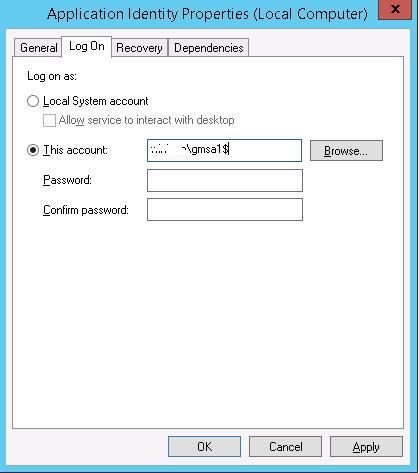
Then in the service properties specify that the service will be run with gMSA account. To do it, check This account in the Log on tab and type the name of the service account. At the end of the name use symbol $, the password need not to be specified. After the changes are saved, the service has to be restarted.
The service account will automatically get the right “Log On As a Service“.
gMSA Fine Tunning
You can change the period of the password change (by default, it is 30 days):
gMSA account can also be used in the Scheduler tasks. A fine nuance is that the task can be configured only in PowerShell:
The argument “-LogonType Password” means that the password of this gMSA account will be obtained from the domain controller.
Set-ADServiceAccount gmsa1-ManagedPasswordIntervalInDays 60gMSA account can also be used in the Scheduler tasks. A fine nuance is that the task can be configured only in PowerShell:
$action = New-ScheduledTaskAction “c:scripts ackup.cmd”$trigger = New-ScheduledTaskTrigger -At 22:00 -Daily$principal = New-ScheduledTaskPrincipal -UserID woshubgmsa1$ -LogonType Password Register-ScheduledTask BackupDB –Action $action –Trigger $trigger –Principal $principalThe argument “-LogonType Password” means that the password of this gMSA account will be obtained from the domain controller.
Note. The gMSA account has to possess “Log on as a batch job” rights.